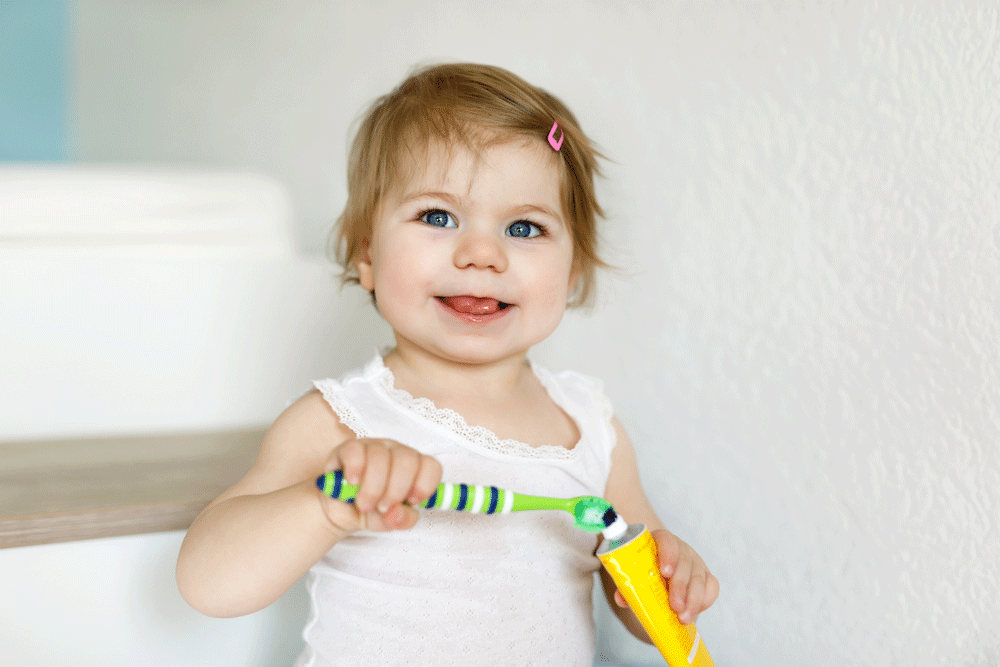
When it comes to caring for your child’s teeth, choosing the right toothpaste is crucial. Children’s oral health needs differ from adults, so it’s essential to select a toothpaste that meets their unique requirements. Pediatric dentists often recommend specific types of toothpaste based on a child’s age, dental health, and developmental stage. In this article, we’ll provide expert advice on choosing the best toothpaste for kids, taking into consideration their oral care needs.
Why Is Choosing the Right Toothpaste for Kids Important?
Children’s teeth are still developing, and their enamel is thinner and more vulnerable than that of adults. Using the wrong type of toothpaste can lead to a variety of dental issues, from poor cavity protection to excess fluoride ingestion. Pediatric dentists emphasize that a proper toothpaste can help prevent cavities, promote healthy gums, and foster a positive dental routine from a young age.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Kids’ Toothpaste
When you’re searching for the best toothpaste for your child, several factors should influence your choice. These include fluoride content, taste, texture, and age appropriateness.
1. Fluoride Content
Fluoride plays a vital role in protecting teeth from decay by strengthening the enamel. For most children aged 2 and older, pediatric dentists recommend a fluoride toothpaste. Fluoride helps to remineralize the enamel, making it more resistant to cavities. However, the amount of fluoride should be monitored. For kids under 3 years old, a rice-sized smear of fluoride toothpaste is enough, while older children can use a pea-sized amount.
2. Age Appropriateness
Different age groups have different needs when it comes to toothpaste. For babies and toddlers (under 2 years), fluoride-free toothpaste is often recommended because they may swallow the paste. Once your child turns 2, you can start introducing fluoride toothpaste, but it’s essential to make sure they’re spitting it out rather than swallowing it. Always look for toothpaste labeled with the appropriate age range to ensure it meets your child’s needs.
3. Taste and Texture
One of the most overlooked but crucial factors is the flavor and texture of the toothpaste. Children tend to be picky about flavors, and if they dislike the toothpaste, they may resist brushing their teeth altogether. Many kids’ toothpastes come in fun flavors like bubblegum or fruit, which can make brushing a more enjoyable experience. Additionally, a smooth texture can help kids with sensory sensitivities feel more comfortable during brushing.
4. ADA Seal of Approval
The American Dental Association (ADA) stamp of approval is a mark of trust. ADA-approved toothpastes have undergone rigorous testing for safety and efficacy, ensuring they’re both effective in preventing cavities and safe for children to use. Always check for the ADA Seal on toothpaste packaging to ensure you’re making a quality choice for your child’s oral care.
Pediatric Dentist Recommendations for Kids’ Toothpaste
Pediatric dentists are trained to understand the specific oral health needs of children, and they can provide valuable insight into selecting the best toothpaste for your little one. Here are some top recommendations from pediatric dentists:
1. Fluoride-Free Toothpastes for Younger Children
For babies and toddlers under 2 years old, fluoride-free toothpaste is usually the best option. These toothpastes typically contain mild ingredients that are safe if accidentally swallowed. Pediatric dentists often recommend options with natural ingredients, like aloe vera or xylitol, which can help clean teeth without introducing harmful chemicals.
2. Low Fluoride Toothpaste for Ages 2-6
Once your child reaches the age of 2, it’s time to start using fluoride toothpaste. However, pediatric dentists recommend that parents use a very small amount to avoid excess fluoride ingestion, which can lead to dental fluorosis. Low-fluoride options that are safe for young children typically contain about 500 to 1000 parts per million (ppm) of fluoride.
3. Fluoride Toothpaste for Kids 6+ Years
For older children who can reliably spit out toothpaste, a higher fluoride content (1000 to 1500 ppm) is recommended. This level of fluoride is effective at fighting cavities and helping maintain healthy teeth. Pediatric dentists also suggest looking for toothpastes that contain calcium and phosphate to help remineralize teeth as they grow.
Tips for Encouraging Good Brushing Habits in Kids
Getting your child into a good oral care routine early on is essential for their long-term dental health. Pediatric dentists offer several tips to make brushing easier and more enjoyable:
-
Make it a Fun Activity: Turn brushing time into a game. You can use a timer, sing a song, or let your child pick out their toothbrush and toothpaste.
-
Supervise Until They’re Old Enough: Even when your child is able to brush on their own, make sure to supervise until they’re around 6 or 7 years old. This ensures they’re brushing properly and not swallowing toothpaste.
-
Positive Reinforcement: Praise your child for brushing well and offer small rewards for consistent brushing habits.
Consulting a Pediatric Dentist Near Me for Personalized Advice
If you’re unsure which toothpaste is best for your child, Consulting a Pediatric Dentist Near Me for Personalized Advice based on your child’s oral health. Pediatric dentists are experts in child dental care and can guide you in selecting the most appropriate toothpaste, along with offering advice on brushing techniques, flossing, and diet. A pediatric dentist will ensure your child’s teeth are properly cared for and help establish lifelong healthy habits.
Conclusion
Choosing the best toothpaste for kids involves balancing fluoride content, age appropriateness, and taste preferences. By consulting with a pediatric dentist and considering your child’s specific needs, you can ensure they have the best oral care possible. Regular brushing, with the right toothpaste, will help protect your child’s teeth from decay, promote good habits, and set them on a path to a lifetime of healthy smiles.